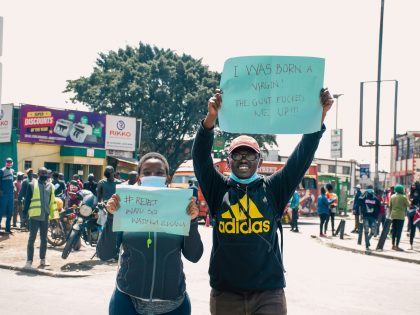#WhiteHistoryMonth

Every February in the U.S. schools, McDonald’s, television, corporations, the advertising industry, celebrate Black History Month. The whole thing is a charade. That black people don’t get a break from police brutality, plain murder, red lining, profiling or plain neglect, whether here, in the UK or places like South Africa, doesn’t matter. In 2007, Gary Younge (he is an ally) suggested that what we all needed is a White History Month. Gary reminded us: “So much of Black History Month takes place in the passive voice. Leaders ‘get assassinated,’ patrons ‘are refused’ service, women ‘are ejected’ from public transport. So the objects of racism are many but the subjects few. In removing the instigators, the historians remove the agency and, in the final reckoning, the historical responsibility … There is no month when we get to talk about [James] Blake [the white busdriver challenged by Rosa Parks]; no opportunity to learn the fates of J.W. Milam and Roy Bryant, who murdered Emmett Till; no time set aside to keep track of Victoria Price and Ruby Bates, whose false accusations of rape against the Scottsboro Boys sent five innocent young black men to jail. Wouldn’t everyone–particularly white people–benefit from becoming better acquainted with these histories?” So, dear readers–in the service of good sense and because we love celebrations–this March is the inaugural White History Month on Africa is a Country. Yes, we’re a few days late, we know, but good things take time some time. Stay tuned.