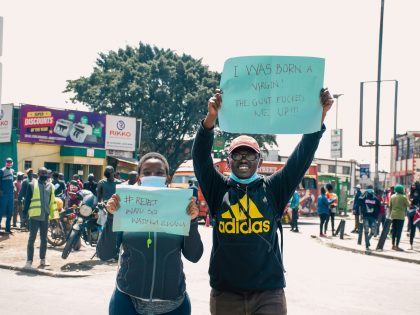Europe’s Eritrean “Problem”
Eritrean refugees — one of the largest groups seeking safety in Europe — have been a primary target of those wanting to close Europe’s borders.

Picturepest, via Flickr CC.
In the aftermath of the Paris attacks, many of Europe’s right wing parties were quick to insinuate Syrian refugees were to blame and to call for stricter immigration and border controls. But even before the attacks, some European governments were already maneuvering to prevent refugees from entering their countries. Eritreans—who represent one of the largest groups of refugees seeking safety in Europe in recent years—have been a primary target of those who would close Europe’s doors.
Efforts to exclude Eritrean refugees from Europe began over a year ago in Denmark. In mid-2014, the Danish Immigration Service embarked on a fact-finding mission to Eritrea after seeing a dramatic rise in the number of Eritreans seeking asylum. The mission report—based primarily on anonymous interviews in Asmara—declared conditions had improved enough that Eritreans would no longer be recognized as refugees in Denmark. Human rights organizations denounced the report, and two men who contributed to it resigned, saying they were pressured to ensure the report allowed Denmark to adopt stricter asylum practices. After a period of public pressure, the Danish government announced Eritreans would still receive asylum in Denmark, but the report remained public.
For over a year, the European Union has also been quietly working with the Eritrean government on stemming migration and calling for, among other things, “promoting sustainable development in countries of origin … in order to address the root causes of irregular migration.” This October, the EU Development Fund announced it was resuming aid to Eritrea with a possible $229 million package for economic development in part to give people alternatives to migration. According to official EU sources, the funding will help tackle poverty and “directly benefit the population.” Such a rationale seemingly ignores that most Eritreans indicate leaving to avoid the regime’s human rights abuses—although officials said such cooperation allows “the EU to reinforce a political dialogue to highlight the importance of human rights.”
Read the rest here.